Table of Contents
ToggleGastroesophageal reflux disease, commonly known as acid reflux, is a digestive disorder in which stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing irritation and discomfort.
While several factors can contribute to the development of acid reflux, stress is often cited as a leading cause.
When the body is under stress, it produces a variety of hormones and chemicals that can weaken the lower esophageal sphincter.
This can lead to symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. Fortunately, there are several home treatments for stress-related heartburn, including relaxation techniques, dietary changes, and over-the-counter medications.
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation.
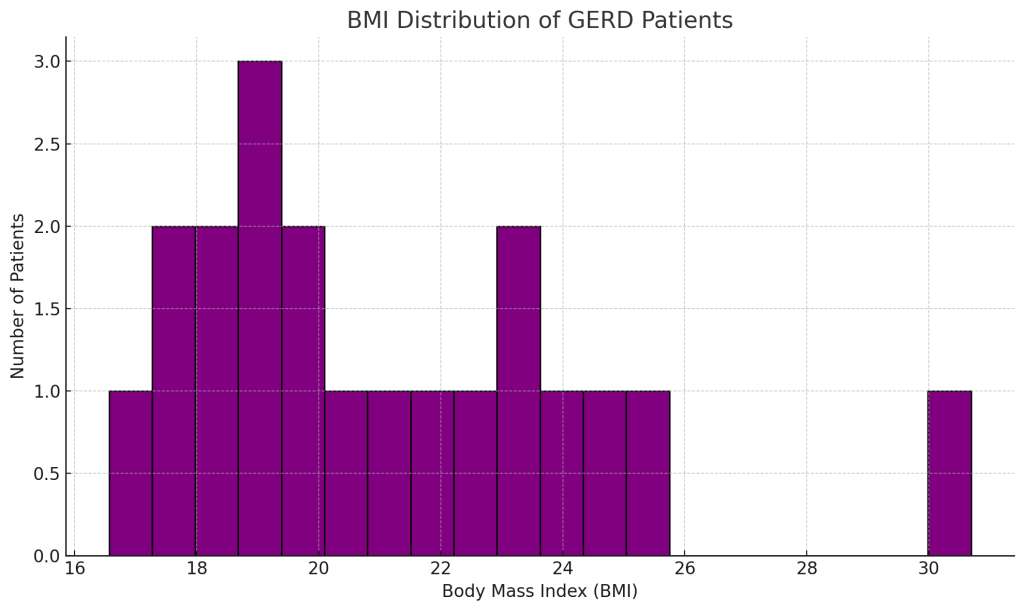
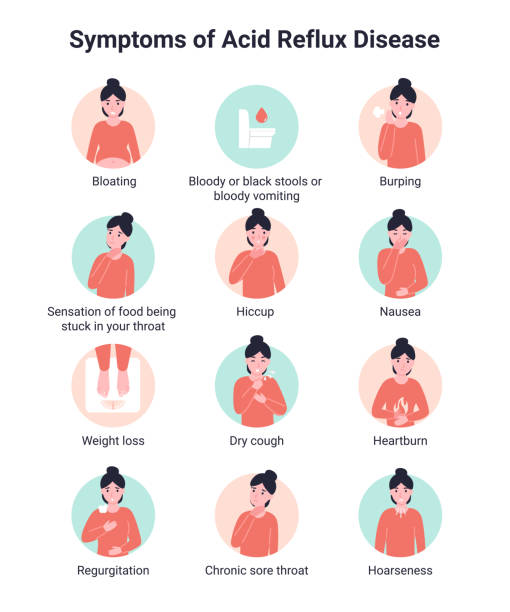
GERD symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. People who experience frequent heartburn are at greater risk of developing GERD, especially if it occurs two or more times a week. Risk factors for GERD include obesity, smoking, and certain medications.
What is stomach acid?
Stomach acid is a digestive fluid produced by the stomach glands to break down food into absorbable nutrients. It is a mixture of hydrochloric acid, enzymes, and mucus that helps to maintain the acidic pH of the stomach.
The acid also serves as a protective barrier against harmful bacteria and parasites. When the stomach produces too much acid or the sphincter muscle between the stomach and esophagus is weakened, stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus, causing heartburn and acid reflux disease.
Treatment options for reflux disease include lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery in severe cases.
Acid Reflux: Causes and Symptoms
Acid reflux is a digestive condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing discomfort and irritation. It occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle at the bottom of the esophagus, fails to close properly.
Common causes of acid reflux include overeating, consuming fatty foods, lying down immediately after a meal, and smoking. In addition, certain medical conditions such as hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can also contribute to acid reflux.
Heartburn symptoms
Typically include a burning sensation in the chest that may worsen after eating or lying down. Other symptoms may include regurgitation, a sour or bitter taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain. Chest pain associated with acid reflux is often described as a squeezing or pressure-like sensation and can be mistaken for a heart attack.
To reduce the risk of acid reflux, it is recommended to avoid fatty or spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. It is also advisable to eat smaller, more frequent meals, and to avoid lying down immediately after eating. If symptoms persist or become more severe, it is important to seek medical attention as untreated acid reflux can lead to complications such as esophagitis or even esophageal cancer.
The Connection between Stress and Acid Reflux
Stress is a common experience that affects many aspects of human physiology, including the digestive system. In the case of acid reflux, the role of the nervous system is critical. The central nervous system controls the digestive processes through a complex network of nerves and hormones. One important aspect of this regulation is stomach acid production. When the nervous system is under stress, it can trigger an overproduction of stomach acid, which can lead to acid reflux.
Role of the Nervous System in Acid Reflux
Life stress and psychological stress are both known to affect the nervous system and contribute to acid reflux. Psychosocial stress, in particular, has been linked to the development of acid reflux symptoms. In some cases, stress can also affect the muscle tone of the esophagus, leading to an increased risk of acid reflux.
Research has shown that there is a strong relationship between stress and acid reflux. In one study, participants who reported high levels of stress in their lives had a significantly higher risk of experiencing acid reflux symptoms. Another study found that psychological factors, such as anxiety and depression, were strongly associated with the severity of acid reflux symptoms.
Effects of Stress on the Digestive System
The regulation of stomach acid production is critically influenced by the nervous system. Psychological stress contributes to the overproduction of acid and the development of acid reflux. More research is required to comprehend the stress-acid reflux relationship, but evidence suggests reducing stress manages symptoms effectively.
How Stress Causes Acid Reflux
Stress is a common trigger for acid reflux. When you experience stress, your body’s natural stress response is activated. This response causes the release of hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, which can impact various bodily functions.
In particular, stress can cause the esophageal sphincter to relax, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Additionally, stress can increase stomach acid production, further exacerbating the problem. This excess acid can irritate the lining of the esophagus and cause the characteristic symptoms of acid reflux, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and a sour taste in the mouth.
If left untreated, chronic acid reflux can lead to complications such as esophagitis and Barrett’s esophagus. Therefore, it’s important to manage stress and find healthy ways to cope with it, in addition to following a treatment plan for acid reflux.
Coping with Stress-Related acid reflux
People who experience stress-related acid reflux often struggle to find relief from their symptoms. However, various lifestyle changes can help reduce stress and improve heartburn symptoms.
Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and meditation can also help reduce stress and prevent heartburn.
Medical treatments for acid reflux
Additionally, medical treatments such as antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 blockers can provide relief for those who experience chronic acid reflux. It’s important to prioritize healthy habits and work with a healthcare provider to find the most effective treatment plan for managing stress-related acid reflux.
Prevention of Stress-Related Acid Reflux
Stress-related acid reflux is a common condition that can be prevented with some simple steps. To avoid heartburn, it is essential to manage stress. To relieve stress, you can try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Over-the-counter medication can also help manage stress-related acid reflux symptoms. It is important to make lifestyle modifications such as getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. Eating a balanced diet that is low in fat and includes plenty of fruits and vegetables can also prevent acid reflux.
Drinking alcohol can trigger acid reflux symptoms, so it is important to limit alcohol consumption. If you experience a burning feeling in your chest, it may be helpful to avoid tight clothing, lying down after eating and eating large meals.
It is also important to avoid eating too close to bedtime as this can trigger heartburn. By making these simple changes to your lifestyle, you can prevent stress-related acid reflux and improve your overall health and well-being.
Tips to avoid acid reflux
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining our physical and mental well-being. When we experience high stress, it can lead to various physical symptoms, including acid reflux. Research suggests that stress can exacerbate the symptoms of heartburn by increasing the production of stomach acid, leading to heartburn, and causing discomfort in the chest and throat. Therefore, it is essential to find ways to manage stress to avoid these symptoms.
One tip to manage stress is to practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation. Another way is to engage in physical activity, like yoga or running, which can help reduce stress and promote overall health. It is also important to take time for yourself and prioritize self-care, such as getting enough sleep, eating a healthy diet, and staying hydrated.
By practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in physical activity, prioritizing self-care, managing your time, and setting boundaries, you can effectively manage stress and avoid acid reflux symptoms.
Role of Diet and Exercise in preventing heartburn
Diet and exercise play a vital role in preventing heartburn. Incorporating low-acid and high-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while avoiding trigger foods like fried and spicy foods, chocolate, and alcohol can help alleviate symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can also reduce the risk of heartburn. Simple activities like walking, yoga, and biking can be effective. Avoiding lying down immediately after eating, wearing loose-fitting clothes, and elevating the head of the bed can also help prevent acid reflux.
By making these small lifestyle changes, individuals can reduce the likelihood of experiencing uncomfortable acid reflux symptoms.